STLC - Software Testing LifeCycle
A well planned process of testing a software/product/application in a systematic way is termed as software testing lifecycle.
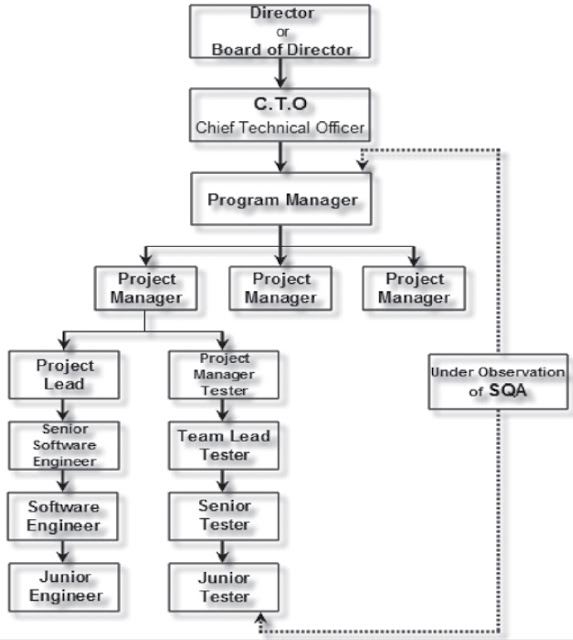
Each and every organization has different phases of STLC. However in general - STLC within waterfall model contains the following phases.
1. Requirements Analysis
2. Test Planning
3. Test Analysis
4. Test Design
5. Test Construction and Verification
6. Testing cycles
7. Final Testing and Implementation
1. Requirements Analysis
In this phase testers analyze the customer requirements and work with developers during the design phase to see which requirements are testable and how they are going to test those requirements.
It is very important to start testing activities from the requirements phase itself because the cost of fixing defect is very less if it is found in requirements phase rather than in future phases.
2. Test Planning
In this phase all the planning about testing is done like what needs to be tested, how the testing will be done, test strategy to be followed, what will be the test environment, what test methodologies will be followed, hardware and software availability, resources, risks etc. A high level test plan document is created which includes all the planning inputs mentioned above and circulated to the stakeholders.
Usually IEEE 829 test plan template is used for test planning.
3. Test Analysis
After test planning phase is over test analysis phase starts, in this phase we need to dig deeper into project and figure out what testing needs to be carried out in each SDLC phase.
Automation activities are also decided in this phase, if automation needs to be done for software product, how will the automation be done, how much time will it take to automate and which features need to be automated.
Non functional testing areas(Stress and performance testing) are also analyzed and defined in this phase.
4. Test Design
In this phase various black-box and white-box test design techniques are used to design the test cases for testing, testers start writing test cases by following those design techniques, if automation testing needs to be done then automation scripts also needs to written in this phase.
5. Test Construction and Verification
In this phase testers prepare more test cases by keeping in mind the positive and negative scenarios, end user scenarios etc. All the test cases and automation scripts need to be completed in this phase and got reviewed by the stakeholders. The test plan document should also be finalized and verified by reviewers.
6. Test Execution and Bug Reporting
Once the unit testing is done by the developers and test team gets the test build, The test cases are executed and defects are reported in bug tracking tool, after the test execution is complete and all the defects are reported. Test execution reports are created and circulated to project stakeholders.
After developers fix the bugs raised by testers they give another build with fixes to testers, testers do re-testing and regression testing to ensure that the defect has been fixed and not affected any other areas of software.
Testing is an iterative process i.e. If defect is found and fixed, testing needs to be done after every defect fix.
After tester assures that defects have been fixed and no more critical defects remain in software the build is given for final testing.
7. Final Testing and Implementation
In this phase the final testing is done for the software, non functional testing like stress, load and performance testing are performed in this phase. The software is also verified in the production kind of environment. Final test execution reports and documents are prepared in this phase.
8. Post Implementation
In this phase the test environment is cleaned up and restored to default state, the process review meeting's are done and lessons learnt are documented. A document is prepared to cope up similar problems in future releases.
Important Links: